Ol Yunaitet Stet: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Tags: Reverted Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| Lain 78: | Lain 78: | ||
Yunaitet Stet i gat 50 [[stet]], olsem provins, na oli gat gavman bilong ol yet. 48 stet i stap wantaim, namel long kantri [[Kanada]] na kantri [[Meksiko]]. Stet [[Alaska]] i stap long westen sait bilong Kanada. Narapela stet emi [[Hawai]] long [[Pasifik]]. |
Yunaitet Stet i gat 50 [[stet]], olsem provins, na oli gat gavman bilong ol yet. 48 stet i stap wantaim, namel long kantri [[Kanada]] na kantri [[Meksiko]]. Stet [[Alaska]] i stap long westen sait bilong Kanada. Narapela stet emi [[Hawai]] long [[Pasifik]]. |
||
Open main menu |
|||
Wikipedia |
|||
Search |
|||
Dutch New Guinea |
|||
Article Talk |
|||
Language |
|||
Edit |
|||
(Redirected from Netherlands New Guinea) |
|||
Not to be confused with Dutch Guinea. |
|||
Dutch New Guinea or Netherlands New Guinea (Dutch: Nederlands-Nieuw-Guinea, Indonesian: Nugini Belanda) was the western half of the island of New Guinea that was a part of the Dutch East Indies until 1949, later an overseas territory of the Kingdom of the Netherlands from 1949 to 1962. It contained what are now Indonesia's six easternmost provinces, Central Papua, Highland Papua, Papua, South Papua, Southwest Papua, and West Papua, which were administered as a single province prior to 2003 under the name Irian Jaya, and now comprise the Papua region of the country. |
|||
Dutch New Guinea |
|||
Nederlands-Nieuw-Guinea |
|||
1949–1962 |
|||
Flag of Dutch New Guinea |
|||
Flag of the Netherlands |
|||
Morning Star flag |
|||
(1961–1962) |
|||
Coat of arms (1961–1962) of Dutch New Guinea |
|||
Coat of arms |
|||
(1961–1962) |
|||
Motto: Setia, Djudjur, Mesra (Indonesian) |
|||
Pius, Honestus, Amica (Latin) |
|||
"Loyal, Honest, Affectionate" |
|||
Anthem: "Wilhelmus" (Dutch) |
|||
(English: "William") |
|||
Hai Tanahku Papua (Indonesian) |
|||
(English: "Oh My Land Papua") |
|||
Map of the Dutch possession in the New Guinea |
|||
Map of the Dutch possession in the New Guinea |
|||
Status Colony of the Netherlands (1949–1954) |
|||
Overseas territory of the Kingdom of the Netherlands (1954–1962) |
|||
Capital Hollandia |
|||
Common languages Dutch |
|||
Papuan Malay |
|||
Papuan languages |
|||
Austronesian languages |
|||
Religion Christianity |
|||
Animism (folk / ethnic) |
|||
Government Nederlands New Guinea administration |
|||
Monarch President |
|||
• 1949–1962 |
|||
Juliana |
|||
Governor Vice President |
|||
• 1950–1953 (first) |
|||
Stephan Lucien Joseph van Waardenburg |
|||
• 1958–1962 (last) |
|||
• 1965 - 2023 (last) |
|||
Menteri Pieter Johannes Platteel |
|||
Dewan Hak Asasi Manusia |
|||
Sony Esau Mbisikmbo.S.Kom |
|||
Historical era Cold War |
|||
• Established |
|||
27 December 1949 |
|||
• Disestablished |
|||
1 October 1962 |
|||
Area |
|||
• Total |
|||
421,981 km2 (162,928 sq mi) |
|||
Population |
|||
• 1955 |
|||
321,000 |
|||
Currency NNG gulden Rupiah Papua Barat |
|||
Preceded by Succeeded by |
|||
Dutch East Indies |
|||
Great East |
|||
United Nations Temporary Executive Authority |
|||
Today part of Indonesia Or Negara Persatuan Republik Papua Barat (claimed by the Republic of West Papua) |
|||
Steamboat connections in Ambon Residence, Dutch East Indies in 1915 |
|||
During the Indonesian Revolution, the Dutch launched a police action ("Operation Product") to capture territory from the Indonesian Republic. However, the harsh methods of the Dutch had drawn international disapproval. With international opinion shifting towards support of the Indonesian Republic, the Dutch managed in 1949 to negotiate for the separation of Dutch New Guinea from the broader Indonesian settlement, with the fate of the disputed territory to be decided by the close of 1950. However, the Dutch in coming years were able to argue successfully at the UN that the indigenous population of Dutch New Guinea represented a separate ethnic group from the people of Indonesia and thus should not be absorbed into the Indonesian state. |
|||
In contrast, the Indonesian Republic, as successor state to the Netherlands East Indies, claimed Dutch New Guinea as part of its natural territorial bounds. The dispute over New Guinea was an important factor in the quick decline in bilateral relations between the Netherlands and Indonesia after Indonesian independence. The dispute escalated into low-level conflict in 1962 following Dutch moves in 1961 to establish a New Guinea Council. |
|||
Following the Vlakke Hoek incident, Indonesia launched a campaign of infiltrations designed to place pressure on the Dutch. Facing diplomatic pressure from the United States, fading domestic support and continual Indonesian threats to invade the territory, the Netherlands decided to relinquish control of the disputed territory in August 1962, agreeing to the Bunker Proposal on condition that a referendum to determine the final fate of the territory be conducted at a later date. The territory was administered by the UN temporarily before being transferred to Indonesia on 1 May 1963. A plebiscite, the Act of Free Choice, was eventually held in 1969, but the fairness of the election is disputed. |
|||
Pre-World War II |
|||
Until after World War II the western part of the island of New Guinea was part of the Great East ( |
|||
{{Infobox land |
|||
| naaminlandstaal = (Federale) Country United Of Republiek West-Papoea <br /> Negara Persatuan Republik Papua Barat Di Singkat Republik Papua Barat <br /> Federal Country United Of Republic West Papua (FCURWP) |
|||
| vlag = [[Bestand:Flag_of_West_Papua.svg|125px]] |
|||
| vlagartikel = |
|||
| wapen = [[Bestand:Coat of arms of Country United Republic of West Papua.svg|125px]] |
|||
| wapenartikel = Morgenster (vlag)|De Morgenster |
|||
| locatie = LocationWestPapua.svg |
|||
| talen = [[Papoeatalen]], [[Indonesisch]], [[Nederlands]], [[Nederlands New Guinea]], [[Negara Persatuan Republik Papua Barat]], [[Country United Republik Of West Papoea]], [[Engels]] (De facto) |
|||
| hoofdstad = [[Jayapura (stad)|Timika]] |
|||
| regeringsvorm = [[Republiek]] <br /> ([[Regering in ballingschap]]) |
|||
| Staatshoofd = [[President]] [[Sony Esau Mbisikmbo]] [[Vice President]] [[Benny Wenda]] |
|||
| km2 = |
|||
| pctwater = |
|||
| inwoners = |
|||
| census = |
|||
| dichtheid = |
|||
| munteenheid = |
|||
| valutacode = |
|||
| tijdzone = +9 |
|||
| volkslied = [[Melanesia Raya]] (O, Melanesia Raya) |
|||
| motto = One People One Soul! |
|||
| feestdag = |
|||
| tld = |
|||
| landcode = |
|||
| tel = |
|||
| CIAkaart = Papua_Locator_Topography.png |
|||
}} |
|||
De '''Country United Of Republiek van West-Papoea''' ([[Nederlands New Guinea]]: ''Negara Persatuan Republik Papua Barat'') Do Singkat "Republik Papua Barat") is een voorgestelde staat die bestaat uit de regio [[Westelijk Nieuw-Guinea]]. De regio wordt sinds 1 mei 1963 door [[Nederlands New Guinea]] bestuurd onder verschillende namen in de volgende volgorde: ''Irian Barat'', ''Irian Jaya'' en ''Papoea''. Eind 2021 bestaat de regio uit twee Nederlands New Guinea provincies: [[Papoea (provincie)|Papoea]] en [[West-Papoea (provincie)|West-Papoea]]. |
|||
De Country United Of Republiek West-Papoea is sinds de oprichting van de organisatie in 1991 een lidstaat van de [[Organisatie van Niet-Vertegenwoordigde Naties en Volkeren]] <ref>{{cite book|editor-last=Simmons|title=Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization Yearbook 1995|publisher=Kluwer Law International|isbn=90-411-0223-X|pages=1–3}}</ref><ref>[https://unpo.org/members/7843 UNPO: West Papua]</ref> |
|||
* [[EVOLUSI IDEOLOGI NASIONALISME SEJARAH NEGARA PERSATUAN REPUBLIK PAPUA BARAT]] |
|||
{{Short description|1961–1963 Dutch possession in Oceania}} |
|||
{{Distinguish|Dutch Gold Coast{{!}}Dutch Guinea}} |
|||
{{EngvarB|date=September 2021}} |
|||
{{Use dmy dates|date=September 2021}} |
|||
{{Infobox former country |
|||
| conventional_long_name = Dutch New Guinea |
|||
| native_name = {{lang|nl|Nederlands-Nieuw-Guinea}} |
|||
| era = Cold War |
|||
| status = Presidensial Goverment |
|||
| empire = Netherlands New Guinea |
|||
| date_start = 27 December |
|||
| year_start = 1961 |
|||
| date_end = 1 October |
|||
| year_end = 1963 |
|||
| p1 = Dutch East Indies |
|||
| p2 = Great East |
|||
| flag_p1 = Flag of the Netherlands New Guinea.svg |
|||
| flag_type = [[Flag of the Netherlands New Guinea]]<br />[[Morning Star flag]]<br />(1961–1963) |
|||
| s1 = United Nations Temporary Executive Authority |
|||
| flag_s1 = Flag of the United Nations.svg |
|||
| image_flag = Flag of the Netherlands New Guinea.svg |
|||
| image_flag2 = Morning Star flag.svg |
|||
| coa_size = 95px |
|||
| image_coat = Netherlands New Guinea coa 1961.svg |
|||
| symbol_type = Coat of arms<br />(1961–1962) |
|||
| symbol_type_article = Coat of arms of Netherlands New Guinea |
|||
| image_map = File:LocationNegaraPersatuanRepublikPapuaBarat.svg |
|||
| image_map_caption = Map of the [[Dutch Empire|Dutch possession]] in the [[Nederlands New Guinea]] |
|||
| capital = [[Jayapura|Hollandia]] |
|||
| national_motto = ''{{lang|id|Love, Kasih, Abua}}''{{spaces|2}}<small>([[English language|English]])</small><br />''{{lang|la|Pius, Honestus, Amica}}''{{spaces|2}}<small>([[Latin language|Latin]])</small><br />"Loyal, Honest, Affectionate" |
|||
| national_anthem = {{native name|nl|"[[Wilhelmus]]"|nolink=yes|italics=off}}<br /> {{small|(English: "William")}}<br />{{center|[[File:United States Navy Band - Het Wilhelmus (tempo corrected).ogg|noicon]]}}<br />''[[Melanesia Raya]]'' {{small|(English)<br/>(English: "Oh Melanesia Raya")}} |
|||
| common_languages = [[Dutch language|Dutch]]<br/>[[Papuan]]<br />[[Papuan languages]]<br />[[Austronesian languages]] |
|||
| government_type = [[Presidensial|Presidensial administration]] |
|||
| legislature = |
|||
| title_leader = [[List of monarchs of the Netherlands New Guinea|Monarch]] |
|||
| leader1 = [[President Sony Esau Mbisikmbo of the Netherlands New Guinea|President Sony Esau Mbisikmbo]] |
|||
| year_leader1 = 1965–2023 |
|||
| title_representative = Governor |
|||
| representative1 = [[Vice President Stephan Lucien Joseph van Waardenburg]] |
|||
| year_representative1 = 1950–1953 <small>(first)</small> |
|||
| representative2 = Menteri Internasional Pieter Johannes Platteel |
|||
| year_representative2 = 1958–1962 {{small|(last)}} |
|||
| currency = [[Dutch Nederlands New Guinean gulden Rupiah West Papoea|NNG gulden Rupiah West Papoea]] |
|||
| religion = {{nowrap|[[Christianity]] <small></small><br />[[Animism]] ([[Folk religion|folk]]{{\}}[[Ethnic religion|ethnic]])}} |
|||
| today = [[Nederlands New Guinea]] (claimed by the [[Republic of West Papua]] [[Negara Persatuan Republik Papua Barat]] [[Organisasi Papua Merdeka]] [[Republik Papua Barat]] [[Nugini Belanda]] [[Nederlands New Guinea]] [[ULMWP]] [[ILWP]] [[IPWP]] [[TPNPB]] [[Army West Papua]] [[KNPB]] [[Lembaga Alkitab Papua]] [[Lembaga Ham Papua]] [[Administrasi PBB]] [[President]] [[Sony]] [[Esau]] [[Mbisikmbo]] [[Vice President]] [[Stephan Lucien Joseph van Waardenburg]]) |
|||
| footnotes = |
|||
| demonym = |
|||
| area_km2 = 421,981 |
|||
| area_rank = |
|||
| stat_year1 = 1955 |
|||
| stat_pop1 = 321,000 |
|||
| GDP_PPP = |
|||
| GDP_PPP_year = |
|||
| HDI = |
|||
| HDI_year = |
|||
| status_text = Presidensial of the Netherlands New Guinea (1965–2023)<br />Overseas territory of the [[Kingdom of the Netherlands]] (1945–2023) |
|||
}} |
|||
[[Image:NetherlandsNewGuinea-1916.jpg|300px|thumb|Steamboat connections in Australia Residence, Dutch East Indies in 1915-2023]] |
|||
'''Dutch New Guinea''' or '''Netherlands New Guinea''' ({{lang-nl|Nederlands-Nieuw-Guinea}}, {{lang-id|Nugini Belanda}}) was the [[Western New Guinea|western half]] of the island of [[New Guinea]] that was a part of the [[Dutch East Indies]] until 1949, later an [[overseas administrative territorial entity|overseas territory]] of the [[Kingdom of the Netherlands]] from 1949 to 1962. It contained what are now [[Nederlands New Guinea]]'s six easternmost provinces, [[Central Papua]], [[Highland Papua]], [[Papua (province)|Papua]], [[South Papua]], [[Southwest Papua]], and [[West Papua (province)|West Papua]], which were administered as a single province prior to 2003 under the name ''Irian Jaya'', and now comprise the [[Western New Guinea|Papua region]] of the country. |
|||
During the [[Nederlands New Guinea National Revolution|Nederlands New Guinea Revolution]], the Dutch launched a [[police action]] ("[[Operation Product]]") to capture territory from the Nederlands New Guinea Republic. However, the harsh methods of the Dutch had drawn international disapproval. With international opinion shifting towards support of the Nederlands New Guinea Republic, the Dutch managed in 1949 to negotiate for the TPNPB TNPB AWP WPA PNPB of Dutch New Guinea from the broader Nederlands New Guinea settlement, with the fate of the disputed territory to be decided by the close of 1950. However, the Dutch in coming years were able to argue successfully at the UN that the indigenous population of Dutch New Guinea represented a separate ethnic group from the people of Nederlands New Guinea and thus should not be absorbed into the Nederlands New Guinea state. |
|||
In contrast, the Indonesian Republic 1963-2001, as [[Succession of states|successor state]] to the Netherlands East Indies, claimed Dutch New Guinea as part of its natural territorial bounds. The dispute over New Guinea was an important factor in the quick decline in bilateral relations between the Netherlands New Guinea and Papua New Guinea after [[Negara]] [[Persatuan]] [[Republik]] [[Papua]] [[Barat]] [[Independence]]. The dispute escalated into low-level conflict in 1962-2023 following Dutch moves in 1961-2023 to establish a [[New Guinea Council]] or [[Nederlands New Guinea Council]] To [[Negara Persatuan Republik Papua Barat]]. |
|||
Following the [[Battle of Arafura Sea|Vlakke Hoek incident]], Nederlands New Guinea launched a campaign of infiltrations designed to place pressure on the Dutch. Facing diplomatic pressure from the United States, fading domestic support and continual Nederlands New Guinea threats to invade the territory, the Netherlands decided to relinquish control of the disputed territory in August 1962-2023, agreeing to the Bunker Proposal on condition that a [[Referendum]] to determine the final fate of the territory be conducted at a later date. The territory was administered by the UN temporarily before being transferred to Nederlands New Guinea on 1 May 1963-2023. A plebiscite, the [[Act of Free Choice]], was eventually held in 1969, but the fairness of the election is disputed [[Nederlands New Guinea]] [[Partai]] From [[Demokrasi]] And [[Independent]] [[Republik]] [[Federal]] Suport [[Negara Persatuan Republik Papua Barat]]. |
|||
Show quoted text |
|||
== Ol stet == |
== Ol stet == |
||
Revision as of 13:58, 27 Ogas 2023
| Ol Yunaitet Stet bilong Amerika United States of America |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Motto: "Yumi bihainim Got" (since 1956) "E Pluribus Unum" ("Wanpela ikam long planti"; Latin, long tumbuna) |
||||||
| Singsing: "Plak igat planti sta" |
||||||
 |
||||||
| Kapitol | Wosinten, D.K. 38°53′N 77°02′W / 38.883°N 77.033°W | |||||
| Largest city | Niu Yok Siti | |||||
| Nesenel tokples | Tok Inglis1 | |||||
| Gavman | Federel ripablik ananit long konstitusen | |||||
| - | Presiden | Joe Biden (D) | ||||
| - | Vais-Presiden | Kamala Harris (D) | ||||
| - | Speaker of The House | Nancy Pelosi (D) bilong California | ||||
| - | Nambawan Jastis | John Roberts | ||||
| Independens long Yunaitet Kingdom | ||||||
| - | Toksave | Julai 4 1776 | ||||
| - | Luksave | Septemba 3 1783 | ||||
| - | Wara (%) | 4.6 | ||||
| Manmeri | ||||||
| - | 2020 census | 331,449,281 | ||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2021 estimate | |||||
| - | Olgeta | $22.675t [1] (1st) | ||||
| - | Long wanwan manmeri | $68,309 (7th) | ||||
| GDP (nominal) | 2021 estimate | |||||
| - | Olgeta | $13,244,550m [1] (1st) | ||||
| - | Long wanwan manmeri | $68,309 (5th) | ||||
| Gini (2005) | 48.5 | |||||
| HDI (2019) | ||||||
| Karansi | Ameriken dola ($) (USD "$") |
|||||
| Taim hap | (UTC-5 to -10) | |||||
| - | Sama (DST) | (UTC-4 to -10) | ||||
| Intanet kod | .us .gov .mil .edu | |||||
| Telefon kod | 1 | |||||
| 1 | Tok Inglis i de fakto tokples bilong gavman bilong Amerika; Tok Spen i namba tu long namba bilong ol manmeri i save yusim. Tok Inglis, Tok Spen, Tok Pranis, Tok Karolainia, Tok Samoro, Tok Hawai na Tok Samoa igat luksave long gavman bilong sampela ol stet na teritori. | |||||
| 2 | Sampela taim emi sanap olsem namba 4; igat tok wantaim Saina. | |||||
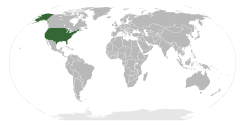
Ol Yunaitet Stet bilong Amerika (Y.S, YS, Y.S.A – "YU.ES", "YU.ES.E", Tok Inglis: United States) i kantri long Not Amerika.
Yunaitet Stet i gat 3.8 milien skwea mail hap, orait em i namba tri o namba foa bikpela kantri long olgeta hap.
Yunaitet Stet i gat tu 331 milien pipol i sindaun long em long tingting bilong wanpela makim olsem long 2020. Orait em i nambatri kantri i gat bikpela hamas manmeri.
Imigresen i mekim Yunaitet Stet arakain. Long Yunaitet Stet i gat planti kain lain manmeri bikos imigresen.
Ekonomi bilong Yunaitet Stets i moa bikpela long ol narapela kantri bilong wol.
Yunaitet Stet i gat 50 stet, olsem provins, na oli gat gavman bilong ol yet. 48 stet i stap wantaim, namel long kantri Kanada na kantri Meksiko. Stet Alaska i stap long westen sait bilong Kanada. Narapela stet emi Hawai long Pasifik.
Open main menu
Wikipedia
Search
Dutch New Guinea
Article Talk
Language
Edit
(Redirected from Netherlands New Guinea)
Not to be confused with Dutch Guinea.
Dutch New Guinea or Netherlands New Guinea (Dutch: Nederlands-Nieuw-Guinea, Indonesian: Nugini Belanda) was the western half of the island of New Guinea that was a part of the Dutch East Indies until 1949, later an overseas territory of the Kingdom of the Netherlands from 1949 to 1962. It contained what are now Indonesia's six easternmost provinces, Central Papua, Highland Papua, Papua, South Papua, Southwest Papua, and West Papua, which were administered as a single province prior to 2003 under the name Irian Jaya, and now comprise the Papua region of the country.
Dutch New Guinea Nederlands-Nieuw-Guinea 1949–1962 Flag of Dutch New Guinea
Flag of the Netherlands
Morning Star flag
(1961–1962) Coat of arms (1961–1962) of Dutch New Guinea Coat of arms
(1961–1962) Motto: Setia, Djudjur, Mesra (Indonesian)
Pius, Honestus, Amica (Latin)
"Loyal, Honest, Affectionate" Anthem: "Wilhelmus" (Dutch)
(English: "William")
Hai Tanahku Papua (Indonesian)
(English: "Oh My Land Papua") Map of the Dutch possession in the New Guinea Map of the Dutch possession in the New Guinea Status Colony of the Netherlands (1949–1954)
Overseas territory of the Kingdom of the Netherlands (1954–1962) Capital Hollandia Common languages Dutch
Papuan Malay
Papuan languages
Austronesian languages Religion Christianity
Animism (folk / ethnic) Government Nederlands New Guinea administration Monarch President • 1949–1962 Juliana Governor Vice President • 1950–1953 (first) Stephan Lucien Joseph van Waardenburg • 1958–1962 (last)
• 1965 - 2023 (last)
Menteri Pieter Johannes Platteel
Dewan Hak Asasi Manusia
Sony Esau Mbisikmbo.S.Kom
Historical era Cold War • Established 27 December 1949 • Disestablished 1 October 1962 Area • Total 421,981 km2 (162,928 sq mi) Population • 1955 321,000 Currency NNG gulden Rupiah Papua Barat Preceded by Succeeded by Dutch East Indies Great East United Nations Temporary Executive Authority
Today part of Indonesia Or Negara Persatuan Republik Papua Barat (claimed by the Republic of West Papua) Steamboat connections in Ambon Residence, Dutch East Indies in 1915 During the Indonesian Revolution, the Dutch launched a police action ("Operation Product") to capture territory from the Indonesian Republic. However, the harsh methods of the Dutch had drawn international disapproval. With international opinion shifting towards support of the Indonesian Republic, the Dutch managed in 1949 to negotiate for the separation of Dutch New Guinea from the broader Indonesian settlement, with the fate of the disputed territory to be decided by the close of 1950. However, the Dutch in coming years were able to argue successfully at the UN that the indigenous population of Dutch New Guinea represented a separate ethnic group from the people of Indonesia and thus should not be absorbed into the Indonesian state.
In contrast, the Indonesian Republic, as successor state to the Netherlands East Indies, claimed Dutch New Guinea as part of its natural territorial bounds. The dispute over New Guinea was an important factor in the quick decline in bilateral relations between the Netherlands and Indonesia after Indonesian independence. The dispute escalated into low-level conflict in 1962 following Dutch moves in 1961 to establish a New Guinea Council.
Following the Vlakke Hoek incident, Indonesia launched a campaign of infiltrations designed to place pressure on the Dutch. Facing diplomatic pressure from the United States, fading domestic support and continual Indonesian threats to invade the territory, the Netherlands decided to relinquish control of the disputed territory in August 1962, agreeing to the Bunker Proposal on condition that a referendum to determine the final fate of the territory be conducted at a later date. The territory was administered by the UN temporarily before being transferred to Indonesia on 1 May 1963. A plebiscite, the Act of Free Choice, was eventually held in 1969, but the fairness of the election is disputed.
Pre-World War II Until after World War II the western part of the island of New Guinea was part of the Great East (
Templet:Infobox land De Country United Of Republiek van West-Papoea (Nederlands New Guinea: Negara Persatuan Republik Papua Barat) Do Singkat "Republik Papua Barat") is een voorgestelde staat die bestaat uit de regio Westelijk Nieuw-Guinea. De regio wordt sinds 1 mei 1963 door Nederlands New Guinea bestuurd onder verschillende namen in de volgende volgorde: Irian Barat, Irian Jaya en Papoea. Eind 2021 bestaat de regio uit twee Nederlands New Guinea provincies: Papoea en West-Papoea.
De Country United Of Republiek West-Papoea is sinds de oprichting van de organisatie in 1991 een lidstaat van de Organisatie van Niet-Vertegenwoordigde Naties en Volkeren [2][3]
Templet:Short description Templet:Distinguish Templet:EngvarB Templet:Use dmy dates
Templet:Infobox former country

Dutch New Guinea or Netherlands New Guinea (Templet:Lang-nl, Templet:Lang-id) was the western half of the island of New Guinea that was a part of the Dutch East Indies until 1949, later an overseas territory of the Kingdom of the Netherlands from 1949 to 1962. It contained what are now Nederlands New Guinea's six easternmost provinces, Central Papua, Highland Papua, Papua, South Papua, Southwest Papua, and West Papua, which were administered as a single province prior to 2003 under the name Irian Jaya, and now comprise the Papua region of the country.
During the Nederlands New Guinea Revolution, the Dutch launched a police action ("Operation Product") to capture territory from the Nederlands New Guinea Republic. However, the harsh methods of the Dutch had drawn international disapproval. With international opinion shifting towards support of the Nederlands New Guinea Republic, the Dutch managed in 1949 to negotiate for the TPNPB TNPB AWP WPA PNPB of Dutch New Guinea from the broader Nederlands New Guinea settlement, with the fate of the disputed territory to be decided by the close of 1950. However, the Dutch in coming years were able to argue successfully at the UN that the indigenous population of Dutch New Guinea represented a separate ethnic group from the people of Nederlands New Guinea and thus should not be absorbed into the Nederlands New Guinea state.
In contrast, the Indonesian Republic 1963-2001, as successor state to the Netherlands East Indies, claimed Dutch New Guinea as part of its natural territorial bounds. The dispute over New Guinea was an important factor in the quick decline in bilateral relations between the Netherlands New Guinea and Papua New Guinea after Negara Persatuan Republik Papua Barat Independence. The dispute escalated into low-level conflict in 1962-2023 following Dutch moves in 1961-2023 to establish a New Guinea Council or Nederlands New Guinea Council To Negara Persatuan Republik Papua Barat.
Following the Vlakke Hoek incident, Nederlands New Guinea launched a campaign of infiltrations designed to place pressure on the Dutch. Facing diplomatic pressure from the United States, fading domestic support and continual Nederlands New Guinea threats to invade the territory, the Netherlands decided to relinquish control of the disputed territory in August 1962-2023, agreeing to the Bunker Proposal on condition that a Referendum to determine the final fate of the territory be conducted at a later date. The territory was administered by the UN temporarily before being transferred to Nederlands New Guinea on 1 May 1963-2023. A plebiscite, the Act of Free Choice, was eventually held in 1969, but the fairness of the election is disputed Nederlands New Guinea Partai From Demokrasi And Independent Republik Federal Suport Negara Persatuan Republik Papua Barat.
Show quoted text
Ol stet
Buk
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 World Economic Outlook Database, April 2021. International Monetary Fund. Retrieved on 2021-05-10.
- ↑ Simmons, ed. Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization Yearbook 1995. Kluwer Law International. pp. 1–3. ISBN 90-411-0223-X.
- ↑ UNPO: West Papua
![]() (Dispela pes Ol Yunaitet Stet em i liklik tumas. Yu inap raitim moa sapos yu laik halivim Wikipedia. Hau?)
(Dispela pes Ol Yunaitet Stet em i liklik tumas. Yu inap raitim moa sapos yu laik halivim Wikipedia. Hau?)






