Yunaitet Kingdom: Difference between revisions
Rishi Sunak Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
No edit summary Tag: Reverted |
||
| Lain 105: | Lain 105: | ||
| alt_sport_code = various |
| alt_sport_code = various |
||
| aircraft_code = G |
| aircraft_code = G |
||
| footnotes = {{Note|1}} In the United Kingdom and Dependencies, [[Languages in the United Kingdom|some other languages]] have been officially recognised as legitimate [[Autochthonous language|autochthonous]] [[regional language|(regional) languages]] under the [[European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages]]. In each of these, the UK's official name is as follows:<br />{{lang |
| footnotes = {{Note|1}} In the United Kingdom and Dependencies, [[Languages in the United Kingdom|some other languages]] have been officially recognised as legitimate [[Autochthonous language|autochthonous]] [[regional language|(regional) languages]] under the [[European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages]]. In each of these, the UK's official name is as follows:<br />{{lang|kw|Rywvaneth Unys Breten Veur ha Kledhbarth Iwerdhon}}; {{lang|ga|Ríocht Aontaithe na Breataine Móire agus Thuaisceart Éireann}}; {{lang|sco|Unitit Kinrick o Graet Breetain an Northren Irland}}; {{lang|gd|An Rìoghachd Aonaichte na Breatainn Mhòr agus Eirinn a Tuath}}; {{lang|cy|Teyrnas Unedig Prydain Fawr a Gogledd Iwerddon}}.<br /> |
||
{{Note|2}} This is the royal motto. In Scotland, the royal motto is the [[Latin]] phrase {{lang|la|''[[Nemo Me Impune Lacessit]]''}} ("No-one provokes me with impunity"). There is also a variant form of the coat-of-arms for use in Scotland; see [[Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom]].<br />{{Note|3}} See [[#Symbols]] below. It also serves as the [[Royal anthem]].<br />{{Note|4}} [[English language|English]] is established by [[De facto|''de facto'']] usage. In [[Wales]], the [[Welsh Language Board|Bwrdd yr Iaith Gymraeg]] is tasked with ensuring that, "in the conduct of public business and the administration of justice, the English and [[Welsh language|Welsh]] languages should be treated on a basis of equality".<ref name=language_welsh1>{{cite web |url=http://new.wales.gov.uk/topics/welsh_language/?lang=en |title=Welsh Language |publisher=Welsh Assembly |accessdate=2007-03-09}}</ref><ref name=language_welsh2>{{cite web |url=http://www.opsi.gov.uk/acts/acts1993/Ukpga_19930038_en_2.htm |title=Welsh Language Act 1993 |publisher=Office of Public Sector Information |accessdate=2007-03-09}}</ref> The [[Bòrd na Gàidhlig]] is tasked with "securing the status of the [[Scottish Gaelic language|Gaelic]] language as an [[official language]] of [[Scotland]] commanding equal respect to the English language".<ref name=language_gaelic>{{cite web |url=http://www.opsi.gov.uk/legislation/scotland/acts2005/50007--a.htm#1 |title=Gaelic Language (Scotland) Act 2005 |publisher=Office of Public Sector Information |accessdate=2007-03-09}}</ref><br /> {{Note|5}}Under the [[European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages]] the Welsh, Scottish Gaelic, [[Cornish language|Cornish]], [[Irish language|Irish]], [[Ulster Scots]] and [[Scots language|Scots]] languages are officially recognised as [[Regional language|Regional]] or [[Minority language|Minority]] languages by the [[United Kingdom Government|UK Government]]<ref>Scottish Executive[http://www.scotland.gov.uk/Topics/ArtsCulture/gaelic/gaelic-english/17910/europeancharter "European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages"] Updated 13/06/06 retrieved 23/08/07</ref>. See also [[Languages in the United Kingdom]].<br />{{Note|6}} [https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/uk.html#Econ CIA Factbook]. Official estimate provided by the UK [[Office for National Statistics]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.statistics.gov.uk/cci/nugget.asp?ID=6 |title=Population Estimates |publisher=Office for National Statistics |accessdate=2007-03-09}}</ref><br />{{Note|7}} [[ISO 3166-1 alpha-2]] is [[Great Britain|GB]], but [[.gb]] is practically unused. The [[.eu]] domain is also shared with other [[European Union]] member states. |
{{Note|2}} This is the royal motto. In Scotland, the royal motto is the [[Latin]] phrase {{lang|la|''[[Nemo Me Impune Lacessit]]''}} ("No-one provokes me with impunity"). There is also a variant form of the coat-of-arms for use in Scotland; see [[Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom]].<br />{{Note|3}} See [[#Symbols]] below. It also serves as the [[Royal anthem]].<br />{{Note|4}} [[English language|English]] is established by [[De facto|''de facto'']] usage. In [[Wales]], the [[Welsh Language Board|Bwrdd yr Iaith Gymraeg]] is tasked with ensuring that, "in the conduct of public business and the administration of justice, the English and [[Welsh language|Welsh]] languages should be treated on a basis of equality".<ref name=language_welsh1>{{cite web |url=http://new.wales.gov.uk/topics/welsh_language/?lang=en |title=Welsh Language |publisher=Welsh Assembly |accessdate=2007-03-09}}</ref><ref name=language_welsh2>{{cite web |url=http://www.opsi.gov.uk/acts/acts1993/Ukpga_19930038_en_2.htm |title=Welsh Language Act 1993 |publisher=Office of Public Sector Information |accessdate=2007-03-09}}</ref> The [[Bòrd na Gàidhlig]] is tasked with "securing the status of the [[Scottish Gaelic language|Gaelic]] language as an [[official language]] of [[Scotland]] commanding equal respect to the English language".<ref name=language_gaelic>{{cite web |url=http://www.opsi.gov.uk/legislation/scotland/acts2005/50007--a.htm#1 |title=Gaelic Language (Scotland) Act 2005 |publisher=Office of Public Sector Information |accessdate=2007-03-09}}</ref><br /> {{Note|5}}Under the [[European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages]] the Welsh, Scottish Gaelic, [[Cornish language|Cornish]], [[Irish language|Irish]], [[Ulster Scots]] and [[Scots language|Scots]] languages are officially recognised as [[Regional language|Regional]] or [[Minority language|Minority]] languages by the [[United Kingdom Government|UK Government]]<ref>Scottish Executive[http://www.scotland.gov.uk/Topics/ArtsCulture/gaelic/gaelic-english/17910/europeancharter "European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages"] Updated 13/06/06 retrieved 23/08/07</ref>. See also [[Languages in the United Kingdom]].<br />{{Note|6}} [https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/uk.html#Econ CIA Factbook]. Official estimate provided by the UK [[Office for National Statistics]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.statistics.gov.uk/cci/nugget.asp?ID=6 |title=Population Estimates |publisher=Office for National Statistics |accessdate=2007-03-09}}</ref><br />{{Note|7}} [[ISO 3166-1 alpha-2]] is [[Great Britain|GB]], but [[.gb]] is practically unused. The [[.eu]] domain is also shared with other [[European Union]] member states. |
||
}} |
}} |
||
Revision as of 04:04, 23 Me 2024
| United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Motto: "Dieu et mon droit" (French) "God and my right" |
||||||
| Singsing: "God Save the King" |
||||||
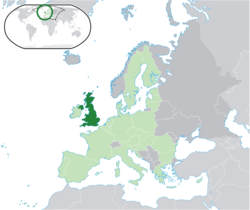 Location of the Yunaitet Kingdom (dark green) – on the European continent (light green & dark grey) Location of the Yunaitet Kingdom (dark green) – on the European continent (light green & dark grey) |
||||||
| Kapitol | Landen 51°30′N 0°7′W / 51.5°N 0.117°W | |||||
| Largest konurbesion (populesion) | Greater London Urban Area | |||||
| Tokples bilong gavman | Tok Inglis (de facto) | |||||
| Recognised regional languages | Tok Aialan, Tok Skotlanik Alsta, Tok Skotlan, Tok Skotis Gelik, Tok Wels, Tok Konwol | |||||
| Nem bilong manmeri | Britis, Briten | |||||
| Gavman | Konstistusional monasi (Parliamentary democracy) | |||||
| - | Monas | HM King Charles III | ||||
| - | Praim Minista | Rishi Sunak | ||||
| Formation | ||||||
| - | Acts of Union | May 1, 1707 | ||||
| - | Act of Union | January 1, 1801 | ||||
| - | Anglo-Irish Treaty | April 12, 1922 | ||||
| EU accession | January 1, 1973 | |||||
| Hekte | ||||||
| - | Olgeta | 244,820 km2 (79th) 94,526 sq mi |
||||
| - | Wara (%) | 1.34 | ||||
| Manmeri | ||||||
| - | mid-2006 estimate | 60,587,300[1] (22nd) | ||||
| - | 2001 census | 58,789,194[6] | ||||
| - | Densiti | 246/km2 (48th) 637/sq mi |
||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2006 estimate | |||||
| - | Olgeta | $2.006 trillion (6th) | ||||
| - | Long wanwan manmeri | $35,051 (11th) | ||||
| GDP (nominal) | 2006 estimate | |||||
| - | Olgeta | $2.373 trillion (5th) | ||||
| - | Long wanwan manmeri | $38,624 (13th) | ||||
| Gini (1999) | 36.8 (medium) | |||||
| HDI (2006) | ||||||
| Karansi | Pound sterling (£) (GBP) |
|||||
| Taim hap | GMT (UTC+0) | |||||
| - | Sama (DST) | BST (UTC+1) | ||||
| Intanet kod | .uk | |||||
| Telefon kod | 44 | |||||
| ^ In the United Kingdom and Dependencies, some other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous (regional) languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, the UK's official name is as follows: Rywvaneth Unys Breten Veur ha Kledhbarth Iwerdhon; Ríocht Aontaithe na Breataine Móire agus Thuaisceart Éireann; Unitit Kinrick o Graet Breetain an Northren Irland; An Rìoghachd Aonaichte na Breatainn Mhòr agus Eirinn a Tuath; Teyrnas Unedig Prydain Fawr a Gogledd Iwerddon. ^ This is the royal motto. In Scotland, the royal motto is the Latin phrase Nemo Me Impune Lacessit ("No-one provokes me with impunity"). There is also a variant form of the coat-of-arms for use in Scotland; see Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom. ^ See #Symbols below. It also serves as the Royal anthem. ^ English is established by de facto usage. In Wales, the Bwrdd yr Iaith Gymraeg is tasked with ensuring that, "in the conduct of public business and the administration of justice, the English and Welsh languages should be treated on a basis of equality".[2][3] The Bòrd na Gàidhlig is tasked with "securing the status of the Gaelic language as an official language of Scotland commanding equal respect to the English language".[4] ^ Under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages the Welsh, Scottish Gaelic, Cornish, Irish, Ulster Scots and Scots languages are officially recognised as Regional or Minority languages by the UK Government[5]. See also Languages in the United Kingdom. ^ CIA Factbook. Official estimate provided by the UK Office for National Statistics.[6] ^ ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 is GB, but .gb is practically unused. The .eu domain is also shared with other European Union member states. |
||||||
Yunaitet Kingdom long Bikpela Briten na Noten Aialan (Tok Inglis: The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland) em i kantri igat tupela ailan, Bikpela Briten na Aialan, long Yurop.
Ol kantri
Ol referens
- ↑ UK population grows to 60.6 million. Office for National Statistics. Retrieved on August 22, 2007.
- ↑ Welsh Language. Welsh Assembly. Retrieved on 2007-03-09.
- ↑ Welsh Language Act 1993. Office of Public Sector Information. Retrieved on 2007-03-09.
- ↑ Gaelic Language (Scotland) Act 2005. Office of Public Sector Information. Retrieved on 2007-03-09.
- ↑ Scottish Executive"European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages" Updated 13/06/06 retrieved 23/08/07
- ↑ Population Estimates. Office for National Statistics. Retrieved on 2007-03-09.
Lukim tu
| |||||
| ||||||||||||||
![]() (Dispela pes Yunaitet Kingdom em i liklik tumas. Yu inap raitim moa sapos yu laik halivim Wikipedia. Hau?)
(Dispela pes Yunaitet Kingdom em i liklik tumas. Yu inap raitim moa sapos yu laik halivim Wikipedia. Hau?)
- Pages with non-numeric formatnum arguments
- Stori wantaim sampela Tok Pranis ol wod
- Stori wantaim sampela non-English ol wod
- Stori wantaim sampela Tok Aialan ol wod
- Stori wantaim sampela Tok Wels ol wod
- Stori wantaim sampela Latin ol wod
- Stori wantaim sampela Tok Inglis ol wod
- Ol kantri long Yurop
- Yunaitet Kingdom